Tjahyaningtijas, Hapsari Peni Agustin (2021) Klasifikasi Tumor Otak Pada Citra MRI Menggunakan en-CNN. Doctoral thesis, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember.
|
Text
DISERTASI_HapsariPeni_cetak.docx - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (3MB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image49.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (95kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image52.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (12kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image27.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (10kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image42.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (95kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image7.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (64kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image57.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (18kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image30.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (24kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image25.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (11kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image51.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (188kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image29.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (7kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image23.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (6kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image44.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (46kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image48.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (35kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image4.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (51kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image60.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (16kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image62.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (54kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image33.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (11kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Other (equation)
image22.wmf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (1kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image10.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (62kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image1.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (38kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image11.wmf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (1kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image17.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (38kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image28.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (10kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image6.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (73kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image63.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (115kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image41.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (6kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image31.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (28kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image9.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (74kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image12.wmf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (954B) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image3.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (142kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image38.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (116kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image71.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (78kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image50.emf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (26kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image32.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (39kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image61.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (31kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image70.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (84kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image35.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (43kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image53.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (14kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image15.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (2kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image14.wmf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (714B) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image24.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (8kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image20.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (12kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image59.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (55kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image40.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (35kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image69.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (83kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image45.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (40kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image37.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (20kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image54.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (111kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image67.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (68kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image56.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (21kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image13.wmf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (2kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image39.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (71kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image34.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (17kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image65.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (21kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image72.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (28kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image47.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (72kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image46.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (148kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image58.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (62kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image5.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (58kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image66.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (66kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Image
image8.png - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only Download (67kB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text (Equation)
image73.wmf - Other Download (67kB) |
|
![[thumbnail of image43.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/75.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image43.png)  Preview |
Image
image43.png Download (28kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image21.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/76.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image21.png)  Preview |
Image
image21.png Download (11kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image2.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/77.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image2.png)  Preview |
Image
image2.png Download (77kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image64.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/78.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image64.png)  Preview |
Image
image64.png Download (47kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image68.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/80.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image68.png)  Preview |
Image
image68.png Download (80kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image19.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/81.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image19.png)  Preview |
Image
image19.png Download (13kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image16.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/82.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image16.png)  Preview |
Image
image16.png Download (18kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image36.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/83.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image36.png) 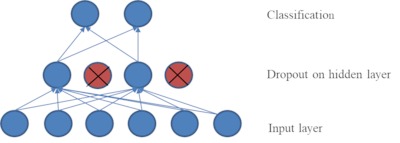 Preview |
Image
image36.png Download (40kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image18.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/85.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image18.png)  Preview |
Image
image18.png Download (10kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image26.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/86.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image26.png)  Preview |
Image
image26.png Download (10kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of image55.png]](https://repository.its.ac.id/87168/87.hassmallThumbnailVersion/image55.png) 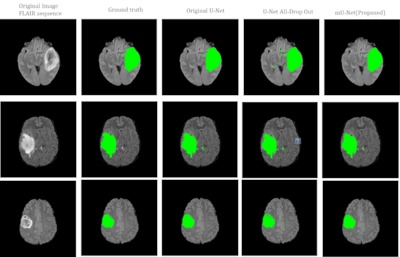 Preview |
Image
image55.png Download (349kB) | Preview |
|
Text
07111760010006-Dissertation.docx Restricted to Repository staff only Download (4MB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text
07111760010006-Dissertation.docx Restricted to Repository staff only Download (4MB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text
07111760010006-Dissertation.docx Restricted to Repository staff only Download (4MB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text
07111760010006-Dissertation.docx Restricted to Repository staff only Download (4MB) | Request a copy |
|
|
Text
07111760010006-Dissertation.pdf - Accepted Version Restricted to Repository staff only until 1 October 2023. Download (3MB) | Request a copy |
Abstract
Tumor otak adalah salah satu penyakit yang paling umum terjadi pada sistem saraf pusat dan sifatnya berbahaya. Diagnosis dini sangat penting untuk perawatan pasien yang tepat. Klasifikasi biner tumor otak yang sering dicirikan dengan tumor otak ganas dan jinak yang melibatkan multi-sekuen MRI (T1, T2, T1CE, dan FLAIR), membuat pekerjaan ahli radiologi membosankan dan rawan terjadinya kesalahan. Pada penelitian ini, dikembangkan metode klasifikasi melalui tahap segmentasi dan metode klasifikasi langsung tanpa mealui tahap segmentasi untuk membantu proses klasifikasi tumor otak oleh ahli. Untuk metode klasifikasi melalui segmentasi, fokus penelitian terdapat pada pengembangan metode segmentasi otomatis untuk segmentasi tumor otak ganas yaitu Glioblastoma (GBM) dan tumor otak jinak yaitu Low Grade Glioma (LGG). Metode segmentasi dikembangkan menggunakan modifikasi U-Net. Arsitektur U-Net dievaluasi berdasarkan jumlah epoch dan nilai drop-out untuk mencapai arsitektur yang paling sesuai. Dari hasil eksperimen, model arsitektur yang paling sesuai untuk segmentasi tumor otak adalah arsitektur modifikasi U-Net atau mU-Net dengan jumlah epoch 90 dan nilai lapisan drop out 0,5. Hasil kinerja segmentasi ditunjukkan dengan nilai dice score sebesar 0,909 yang lebih besar dari penelitian sebelumnya. Metode segmentasi yang diusulkan mampu meningkatkan akurasi klasifikasi tumor otak sebesar 95,65% menggunakan DNN. Nilai akurasi tersebut 2,7% lebih tinggi dari pada jika menggunakan metode SVM yaitu sebesar 92,9%.
Dilain pihak, beberapa metode klasifikasi berdasarkan deep learning digunakan untuk mengklasifikasikan tumor otak. Performa masing-masing model sangat bergantung pada arsitektur CNN yang digunakan. Karena kompleksitas arsitektur CNN yang ada, penyetelan hyperparameter menjadi masalah dalam penerapannya. Pada penelitian ini diusulkan metode CNN yang disebut dengan en-CNN untuk mengatasi masalah ini. Metode ini didasarkan pada VGG-16 yang terdiri dari tujuh jaringan konvolusi, empat ReLU, dan empat max-pooling. Metode yang diusulkan digunakan untuk memfasilitasi penyetelan hyperparameter. Metode ini merupakan pendekatan dimana klasifikasi tumor otak dilakukan secara langsung tanpa terlebih dahulu melakukan proses segmentasi. Pendekatan baru terdiri dari tahapan berikut: preproses, augmentasi citra, dan penerapan metode en-CNN. Klasifikasi tumor otak dilakukan menggunakan empat sekuen MRI T1, T1CE, T2, dan FLAIR. Metode yang diusulkan memberikan akurasi pada dataset MRI multi-sekuen BraTS 2018 dengan akurasi 95,5% untuk T1, 95,5% untuk T1CE, 94% untuk T2, dan 97% untuk FLAIR dengan ukuran mini-batch 128 dan epoch 200 menggunakan fungsi optimasi ADAM. Akurasinya 4% lebih tinggi dari penelitian sebelumnya dalam dataset yang sama.
=====================================================================================================
Brain tumors are one of the most common diseases of the central nervous
system and are dangerous in nature. Early diagnosis is essential for proper patient
care. Radiologists need an automated system to identify brain tumor images. The
tumor identification process is a tedious and error-prone task. In addition, the binary
classification of brain tumors which are often characterized by malignant and
benign brain tumors involving multi-sequence MRI (T1, T2, T1CE, and FLAIR),
makes the work of radiologists quite challenging. In this study, a classification
method was developed through the segmentation stage. and the direct classification
method without going through the segmentation stage. For the classification method
through segmentation, the research focus is on the development of automatic
segmentation methods using U-Net modifications. The U-Net architecture was
evaluated based on the number of epochs and drop-out values to achieve the most
suitable architecture for automatic segmentation of glioblastoma brain tumors.
From the experimental results, the most suitable architectural model for brain tumor
segmentation is the mU-Net architecture with 90 epochs and a dropout layer value
of 0.5. The results of segmentation performance are indicated by a dice score of
0.909, which is greater than the previous study. Using DNN, the proposed
segmentation method can improve the accuracy of brain tumor classification by
95.65%. The accuracy value is 2.7 % higher than 92.9 % when using the SVM
method.
On the other hand, several classification methods based on deep learning are
used to classify brain tumors. The performance of each model is highly dependent
on the CNN architecture used. Due to the complexity of the existing CNN
architecture, hyperparameter tuning is a problem in its implementation. In this
study, a CNN method called en-CNN is proposed to overcome this problem. This
method is based on VGG-16 which consists of seven convolution networks, four
ReLUs, and four max-poolings. The proposed method is used to facilitate
hyperparameter tuning. This method is an approach where the classification of brain
tumors is done directly without first doing the segmentation process. The new
approach consists of the following stages: preprocessing, image augmentation, and
application of the en-CNN method. Brain tumor classification was performed using
four MRI sequences T1, T1CE, T2, and FLAIR. The proposed method provides an
accuracy of the 2018 BraTS multi-sequence MRI dataset with an accuracy of 95.5%
for T1, 95.5% for T1CE, 94% for T2, and 97% for FLAIR with mini-batch sizes of
128 and epoch 200 using the function ADAM optimization. The accuracy is 4%
higher than previous studies in the same dataset
| Item Type: | Thesis (Doctoral) |
|---|---|
| Additional Information: | - |
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Segmentasi tumor otak, U-Net, drop-out, dice score, hyperparameter, Brain tumor segmentation, U-Net, drop-out, dice score, hyperparameter |
| Subjects: | T Technology > T Technology (General) > T57.5 Data Processing T Technology > T Technology (General) > T57.8 Nonlinear programming. Support vector machine. Wavelets. Hidden Markov models. T Technology > T Technology (General) > T58.5 Information technology. IT--Auditing |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Intelligent Electrical and Informatics Technology (ELECTICS) > Electrical Engineering > 20001-(S3) PhD Thesis |
| Depositing User: | Hapsari Peni Agustin Tjahyaningtijas |
| Date Deposited: | 17 Aug 2021 06:56 |
| Last Modified: | 23 Sep 2025 08:11 |
| URI: | http://repository.its.ac.id/id/eprint/87168 |
Actions (login required)
 |
View Item |